Publications
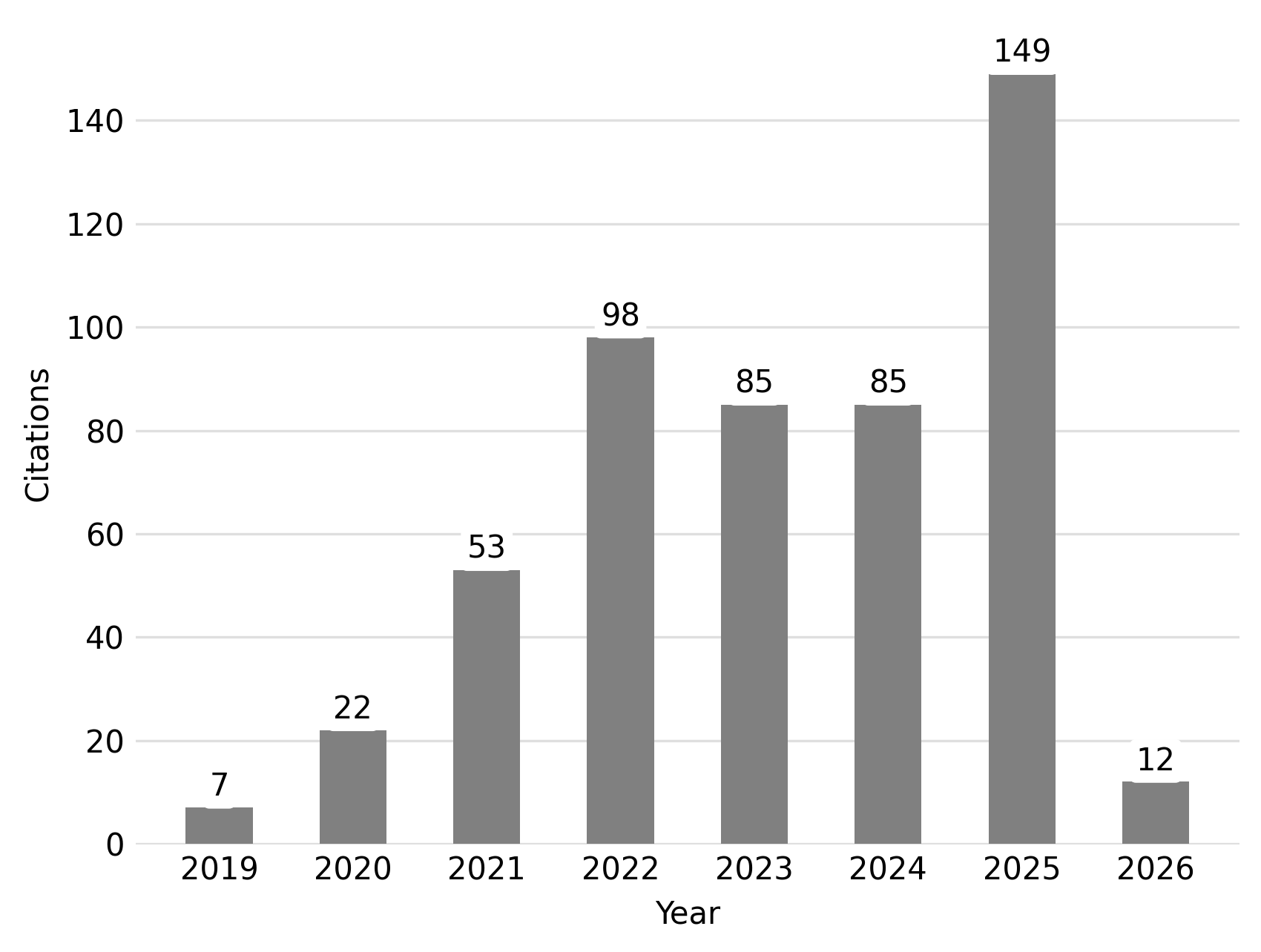
Citations by year (center)
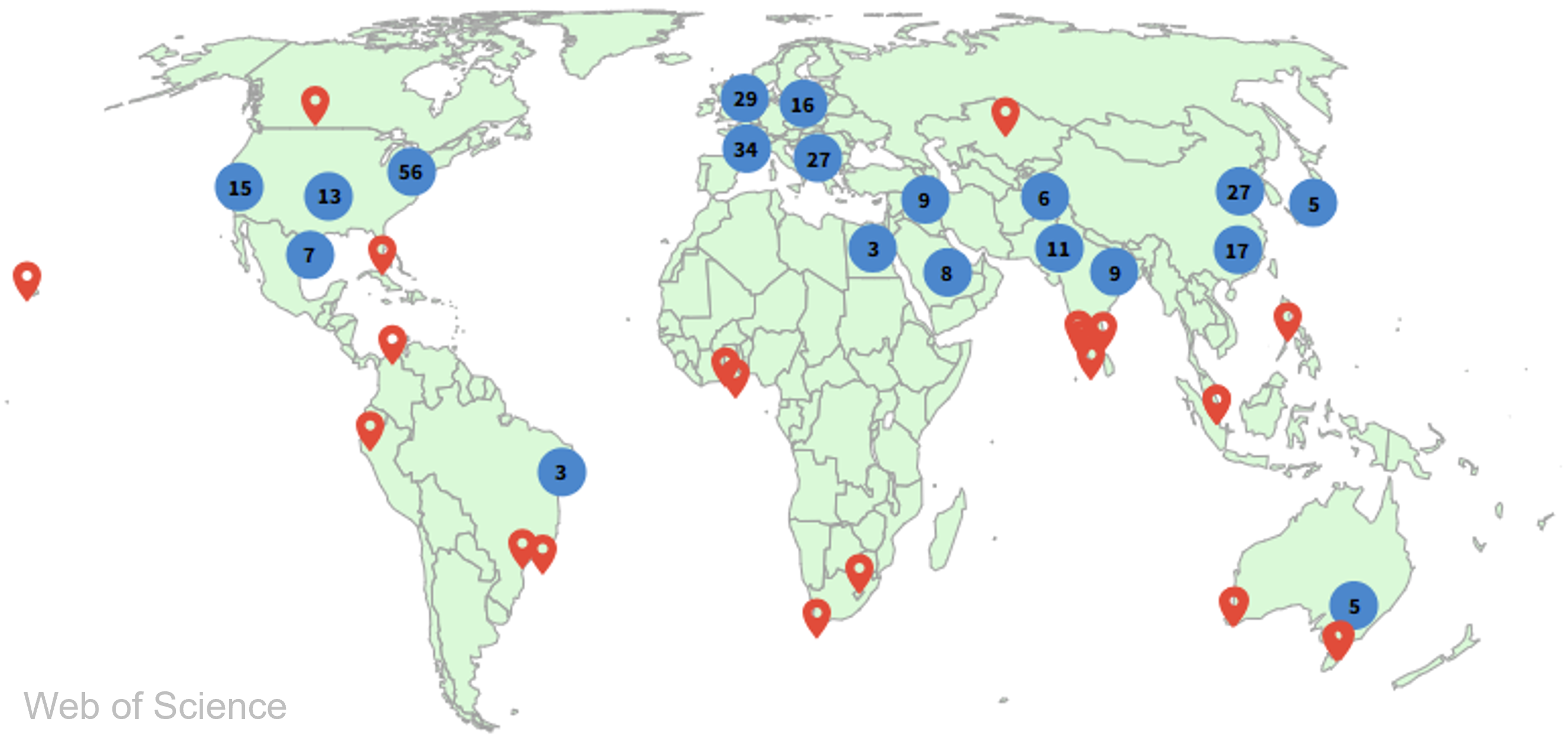
Citations by location (far right)
Published
18. Multi-objective optimization of process parameters for part quality with laser powder bed fusion: a heat exchanger application
ASME J. Mech. Des. | December 2025
This study presents an approach for optimizing the additive manufacturing (AM) process parameters to achieve desired part quality in laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). By optimizing three process parameters (layer thickness, laser power, and scanning speed), we improve geometric accuracy by 19% and reduce porosity by 0.2%.
17. Automated metrology for additively manufactured parts using deep learning and computer vision
Proc. SPIE 13572, Automated Visual Inspection and Machine Vision | August 2025
We develop a fully automated metrology pipeline using deep learning techniques for dimension analysis of additively manufactured parts. Our research employs Line Segment Detector (LSD) and CNN-based Ellipse Detector (EIDet) to accurately extract and measure geometric features from image data without manual intervention. This approach demonstrates robust generalizability across diverse geometries, achieving high accuracy with reduced runtime compared to traditional methods.
16. Additive manufacturing source identification from photographs using deep learning
npj Advanced Manufacturing | May 2025 | 3D-printing-industry, Scienmag, Engineering.com
We show that every 3D printer has a unique “fingerprint” that is imprinted on the parts it manufactures. By utilizing images and deep learning, we can read this fingerprint and accurately identify the specific machine that produced a given part. Our technique provides critical insights for customers and manufacturers, and enables innovative methods for part authentication, counterfeit detection, and quality management strategies.
15. Multi-objective surrogate optimization of process parameters for additive manufacturing with applications in laser powder bed fusion
Proc. ASME IDETC-CIE: Vol. 3A | November 2024
We propose an optimization-based approach for selecting additive manufacturing (AM) process parameters for high quality parts made using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). By optimizing three process parameters (layer thickness, laser power, and scanning speed), we achieved 17% better geometric accuracy while meeting porosity requirements. Our results reveal that laser power is the most influential parameter affecting both geometric accuracy and porosity.
Manufacturing Letters | October 2024
Journal of Manufacturing Systems | June 2024
Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing | May 2024 | Selected Press: AZO-materials, NovusLight
Additive Manufacturing Letters | April 2024
10. Using machine learning to predict dimensions and qualify diverse part designs across multiple additive machines and materials
Additive Manufacturing | July 2022 | Selected Press: nanoHub
J. of Materials Processing Technology | April 2022
Additive Manufacturing | January 2022
Joule | September 2021 | Selected Press: ASME, 3D-printing-industry
ASME J. of Medical Diagnostics | May 2021
Additive Manufacturing | April 2021 | Selected Press: Press Release
PLOS ONE | December 2020 | Selected Press: UIUC RapidVent
Additive Manufacturing | August 2019
Additive Manufacturing | January 2019 | Selected Press: 3Dprint.com
Proc. SPIE 10040, Endoscopic Microscopy XII | February 2017 | Selected Press: SPIE
Patents
- T.C. Gossett, G.T. Pinto, C.D. Wood, D.J. McGregor, and W.P. King. “De-identified search of part designs.” U.S. Patent 12,462,262 B2, Nov. 04, 2025.
- T.C. Gossett, G.T. Pinto, C.D. Wood, D.J. McGregor, and W.P. King. “De-identified search of part designs.” U.S. Patent 12,443,964 B2, Oct. 14, 2025.
- W.P. King, S. Tawfick, M. Bimrose, C. Wood, and D.J. McGregor. “Conformance testing of manufactured parts via neural networks.” U.S. Patent 12,125,190 B1, Oct. 22, 2024.
Can't access a paper? Send an email to mcgregor@umd.edu with the subject line “Paper Request” and we will share downloadable copies with you shortly.
You may also find some of the Author Accepted Manuscripts (AAMs) freely available in the Digital Repository at the University of Maryland (DRUM).
Updated: December 11, 2025

















